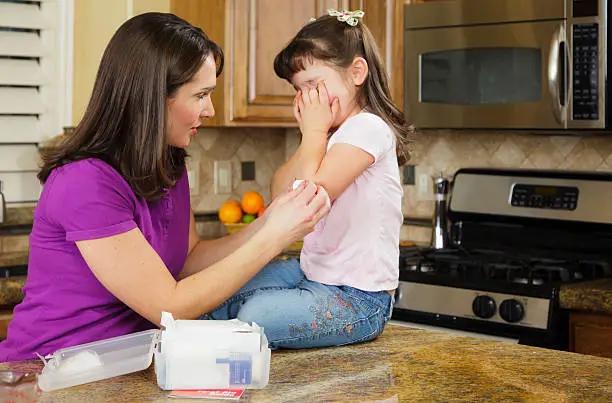
Bee stings, while often a temporary discomfort, can occasionally lead to severe reactions in some individuals. In such cases, knowing how to administer emergency first aid is crucial. Swift and appropriate action can make a significant difference in reducing the severity of symptoms and preventing complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will outline a step-by-step approach to emergency first aid for bee stings, covering everything from initial assessment to effective treatment.
1. Assess the Situation: Remain Calm and Evaluate the Threat
The first step in responding to a bee sting is to assess the situation calmly. Ensure that you and the affected person are out of immediate danger. If the person has been stung multiple times or is showing signs of a severe allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a rapid heartbeat, call for emergency medical assistance immediately.
2. Remove the Stinger: Act Quickly and Carefully
When a bee stings, it leaves behind a stinger embedded in the skin, along with a venom sac that continues to release venom. Quick removal of the stinger is crucial to limit the amount of venom injected. Use a tweezer or the edge of a credit card to scrape the stinger away gently. Avoid using tweezers if possible, as squeezing the stinger can release more venom.
3. Wash the Area: Cleanse to Prevent Infection
After removing the stinger, wash the affected area with mild soap and water to reduce the risk of infection. Be gentle to avoid further irritation. Pat the area dry with a clean cloth.
4. Apply a Cold Compress: Reduce Pain and Swelling
The next step is to apply a cold compress or ice pack to the sting site. This helps numb the area, alleviating pain, and reduces swelling by constricting blood vessels. Wrap the ice pack in a thin cloth to prevent frostbite and apply it to the affected area for 10-15 minutes.
5. Elevate the Limb: Minimize Swelling
If the bee sting is on an extremity, such as an arm or leg, elevate it to minimize swelling. This can be especially helpful if the sting occurs on the hand or foot. Elevating the limb helps reduce blood flow to the affected area, decreasing swelling.
6. Administer Pain Relief: Over-the-Counter Options
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can be administered according to the manufacturer’s instructions to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. However, it’s important to ensure that the affected person is not allergic to these medications and does not have any contraindications.
7. Monitor for Allergic Reactions: Stay Vigilant
Keep a close eye on the person who has been stung for any signs of an allergic reaction. Symptoms of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) may include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, a rapid or weak pulse, and a drop in blood pressure. If any of these symptoms occur, seek emergency medical help immediately.
8. Use Antihistamines: Address Allergic Reactions
If the person stung has a known allergy to bee stings and carries an epinephrine auto-injector, administer it according to their prescription and seek emergency medical attention immediately. In the absence of an epinephrine auto-injector, an oral antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine, can help alleviate mild allergic reactions. Again, it’s essential to ensure the person is not allergic to the antihistamine.
9. Stay Hydrated: Support Recovery
Encourage the affected person to stay hydrated by drinking water. Hydration is crucial for overall well-being and can aid in the recovery process. Avoid alcohol and caffeinated beverages, as they can contribute to dehydration.
10. Seek Medical Attention if Needed: Know When to Call for Help
While many bee stings can be managed with the steps outlined above, some situations require prompt medical attention. If the person experiences a severe allergic reaction, has been stung multiple times, or if symptoms persist or worsen, seek emergency medical help immediately. Do not hesitate to call for assistance if you are unsure about the severity of the reaction.
11. Use Calamine Lotion or Hydrocortisone Cream: Soothe Itching
For those experiencing persistent itching after a bee sting, calamine lotion or over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream can be beneficial. These products can help alleviate itching and provide additional relief from inflammation. Apply a thin layer to the affected area following the instructions on the product packaging.
12. Consider Natural Remedies: Explore Additional Options
In addition to conventional first aid measures, some individuals find relief from natural remedies. Applying a paste made from baking soda and water or aloe vera gel to the sting site can have a soothing effect. Keep in mind that while these remedies may work for some, their effectiveness can vary, and it’s crucial to prioritize scientifically validated methods.
13. Monitor for Secondary Infections: Watch for Signs
Even with proper first aid, bee stings can occasionally lead to secondary bacterial infections. Monitor the sting site for any signs of infection, such as increasing redness, swelling, or the presence of pus. If these symptoms develop, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and potential antibiotic treatment.
14. Understand Individual Sensitivities: Allergic Reactions Vary
Individuals can have varying sensitivities to bee venom, and reactions may change over time. Someone who has not previously shown signs of an allergic reaction might experience one with subsequent stings. It’s essential to be aware of individual sensitivities and seek medical attention promptly if there is any suspicion of an allergic response.
15. Practice Prevention: Be Mindful in Bee-Prone Areas
Prevention is the best form of first aid when it comes to bee stings. Be mindful of your surroundings, especially in areas where bees are likely to be present. Avoid wearing bright-colored clothing and floral-scented perfumes, as these can attract bees. When dining outdoors, keep food and sugary drinks covered, and promptly clean up any spills to avoid attracting these buzzing insects.
16. Educate Yourself on Allergies: Know the Signs
Understanding the signs of an allergic reaction to a bee sting is crucial. Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe, and recognizing the symptoms early can make a significant difference in the outcome. Educate yourself and those around you on the signs of anaphylaxis, and be prepared to take swift action if needed.
17. Know When to Use an Epinephrine Auto-Injector: Carry it if Prescribed
For individuals with known severe allergies to bee stings, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector is essential. Ensure that the device is not expired, and know how to use it in case of an emergency. The epinephrine auto-injector can buy valuable time until professional medical help arrives.
18. Stay with the Person: Provide Emotional Support
Beyond the physical aspects of first aid, emotional support is crucial. Stay with the person who has been stung, especially if they are experiencing anxiety or distress. Reassure them and keep them calm while waiting for medical assistance, if necessary.
19. Document the Incident: Note Details for Medical Professionals
If professional medical attention is sought, provide healthcare professionals with as much information as possible. Note the time of the sting, the location, and any first aid measures administered. Details about the person’s medical history, including known allergies, can assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions about treatment.
20. Follow Up: Monitor for Delayed Reactions
Even after the initial sting and first aid, it’s crucial to monitor for delayed reactions. Some individuals may experience a delayed onset of symptoms, including generalized itching, hives, or swelling away from the sting site. If such symptoms occur, seek medical attention promptly.
In conclusion, emergency first aid for bee stings involves a multifaceted approach, from prompt removal of the stinger to managing symptoms and being vigilant for signs of allergic reactions. Preparedness, calmness, and quick action can significantly impact the outcome. However, it’s important to recognize that severe reactions can occur, and professional medical assistance should be sought when needed. By incorporating these additional steps into your first aid knowledge, you can enhance your ability to respond effectively to bee stings and contribute to the well-being of those around you.






Bee Sting Relief Effective Treatments and Quick Remedies
Beyond Honey: Surprising Solutions for Bee Sting Pain
The Importance of Quick Action: Treating Bee Stings at Home
Emergency First Aid for Bee Stings: A Step-by-Step Guide